What is Mean Platelet Volume
Mean platelet volume (MPV) is part of the Complete Blood Count (CBC) test. It measures the average size of platelets in the blood of the patient.
The test is specifically used to analyze the relationship between the production of platelets in the bone marrow and the destruction/consumption of the same.
Platelets are important components of the blood mainly involved in the blood clotting process.
The following are important aspects about mean platelet volume.
MPV Blood Test
1. Mean platelet volume detects blood disorders
The platelet count test, which is a different procedure, is used to screen whether or not the body has sufficient amount of circulating platelets. It can also reflect the status of platelet production in the bone marrow.
For example, a low or high platelet count will give a hint that the individual has developed abnormal levels which may be associated with an underlying blood disorder or medical condition. Changes in platelet count may also be connected to a dysfunction in the bone marrow where the cell fragments are produced.
In comparison to platelet count, mean platelet volume is used to help achieve a direct distinctive diagnosis between the different causes of thrombocytopenia, diseases of the bone marrow, and other bleeding disorders before it becomes evident with use of platelet counting. Abnormal results on reports may either read as mean platelet volume low or mean platelet volume high.
A high MPV means you have larger platelet size than normal while low MPV suggests a size that is smaller and older than normal. The main objective in carrying out both tests is the detection and monitoring of specific disease activities in the blood, particularly relevant to the status of platelets.
2. A normal MPV has a range of 7.5-11.5 femtoliters
A level of 7.5-11.5 femtoliters (one quadrillionth of a liter) is the normal range for mean platelet volume in most cases. However, the range is subject to some factors.
In order to determine the most favorable normal range for a specific group of people, there are aspects that must be considered. One factor, in particular, is the geographical area where the individual resides. For instance, people in the Mediterranean region have shown to display a higher MPV than those in some other geographical regions.
3. High MPV + Low Platelet Count
High Mean Platelet Volume (high MPV) with a low platelet count signifies a condition where massive destruction of platelets in the blood is present. Medical disorders that may have developed include immune thrombocytopenia, a condition in which the immune system of the individual abnormally attacks the platelets being formed, destroying them.
In the same context, during pregnancy, a condition known as pre-eclampsia may be experienced. This is a disorder where the blood pressure of the pregnant woman becomes elevated to abnormal levels. However, the condition usually becomes better after the birth of the child and consequently returns to normal after some time.
- Xiucui Han, Pengfei Xu, Xiuzhi Duan, Yongxia Liu, Junfeng Zhang, & Hui Xu (2019). High mean platelet volume‑to‑platelet count ratio as a diagnostic maker for increased risk of liver function damage in pediatric patients with infectious mononucleosis in China.
- Deonilson Schmoeller1, Maria Mercedes Picarelli, Terezinha Paz Munhoz, Carlos Eduardo Poli de Figueiredo, & imageHenrique Luiz Staub (2017). Mean Platelet Volume and Immature Platelet Fraction in Autoimmune Disorders.
4. High MPV + Normal Platelet Count
High Mean Platelet Volume (high MPV) with normal platelet count can be a sign of chronic myeloid leukemia, a condition where there is an overproduction in a particular type of white blood cells.
A medical disorder known as hyperthyroidism may also be evident when MPV is high with the platelet count at normal levels. It is a condition that displays excessive production of thyroid hormones.
5. Low MPV due to certain drugs
There can be cases where the MPV is lower than average level. A Low Mean Platelet Volume (low MPV) mostly results from therapies that involve usage of drugs that are toxic to cells, either directly killing the platelets or destroying the megakaryocyte cells in the bone marrow. The megakaryocytes are the precursors necessary in the production of platelets.
When accompanied with normal platelet count, the low MPV suggests chronic kidney failure. If the low mean platelet volume level is accompanied with high platelet count, it reflects an underlying infection of body cells or indicates that the person has a certain form of cancer.
6. High MPV may result to blood clumping
When High MPV is accompanied with a high platelet count, it shows that the bone marrow is producing platelets in excess. Abnormal MPV does not only help identify underlying conditions that merit further investigation or confirm medical conditions, but are also indicative of being a threat in itself.
A high MPV for instance, may indicate that the amount of platelets in the blood is higher than the normal levels, implying that the platelets have developed a higher tendency of clotting and clumping together. This condition places the person at risk of medical conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, stroke, or thrombosis.
In such situations, aspirin may be prescribed having a capacity to prevent the clumping together of platelets in forming blood clots.
7. Low MPV may result to excessive bleeding
In some patients, the Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) is way lower below the normal Mean Platelet Volume (MPV), indicating that the process of blood clotting may be impaired. These individuals should be advised of precautions against the intake of aspirin.
- X.H. Xu, J.W. Yu, X.R. Yu, & Y.G. Huang (2018). Low mean platelet volume is an independent risk factor for increased blood loss in radical hysterectomy.
- Bashir Abdrhamn Bashir Mohamed (2018). Mean platelet volume a marker for bleeding risk; a prospective study among Sudanese patients with dengue virus infection.
8. MPV indicates platelet reactivity
Besides the determination of platelet size, Mean Platelet Volume can also be used to identify reactivity of platelets. This can be seen on the resulting level of platelets turnover.
An elevated MPV is a good indicator to suggest the presence of larger and more reactive platelets which is likely a result of increased platelet turnover. This represents a risk of overall vascular mortality including myocardial infarction.
Individuals with an increased MPV are more likely to end up with blood disorders that may consequently result in death.
9. MPV as a prognostic marker
Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) can also be useful in understanding the course of some clinical conditions such as stroke and ischemic bowel disease. It can be used as a prognostic marker to determine whether the outcome in patients with these conditions will be favorable or unfavorable.
It has been observed in past patients with a higher prevalence of stroke to have a mean platelet volume more than 9.4 fL. A higher MPV is mostly seen as an indicator of poor outcome in patients with both the previously mentioned conditions.
10. MPV is affected by some cardiovascular factors
Some cardiovascular risk factors such as smoking and hypertension can greatly influence MPV, based on the confounding factors like low-grade inflammation. There is a confirmed correlation between increased MPV and the risk of thrombosis.
High MPV can be connected to various established risks, cardio- and cerebrovascular disorders, as well as low-grade inflammatory disorders vulnerable to venous and arterial thrombosis.
- Ozgur Surgit, Hamdi Pusuroglu, Mehmet Erturk, Ozgur Akgul, Ali Buturak, Emre Akkaya, Mehmet Gul, Begum Uygur, Serkan Yazan, & Abdurrahman Eksik (2015). Assessment of Mean Platelet Volume in Patients with Resistant Hypertension, Controlled Hypertension and Normotensives.
- KAZUOMI KARIO, TAKEFUMI MATSUO, & KAZUKIYO NAKAO (1992). Cigarette smoking increases the mean platelet volume in elderly patients with risk factors for atherosclerosis .
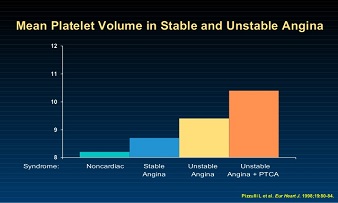
From several medical research activities, it is evident that patients with an increased MPV of more than 11.01 fL are at a higher risk of blood complications and death due to a condition called ischemic heart disease. Dangerous ratios usually result from obesity or smoking.
- READ MORE