Thrombocytosis is an indication that a person has excessive platelets in the blood. The high platelet count can lead to abnormal clotting of blood in the blood vessels. This can be a serious problem considering that the blood vessels facilitate the way for movement of blood around the body.
The eye is not an exception to abnormal blood clotting. A blood clot in the eye, also known as retinal vascular occlusion, is a disorder that affects small veins of the eye, specifically troubling the retina.
It results from an existing obstruction that occurs in the veins or arteries that carry blood to or from the eye’s retina. The obstruction is typically caused by a blood clot.
The blockage can sometimes occur in the main vein or artery, resulting to more serious sight problems, compared to those that occur in branches of veins and arteries of the eye’s retina.
An obstruction of the blood’s way of passage in the vein or artery of the eye’s retina results to blood or other fluids to build up within blood vessels. In the process, the retina becomes inhibited from performing its role of filtering light properly.
With a blocking of the light, and the presence of fluids that are supposed to circulate, sudden loss of vision may occur. The degree of severity when it comes to losing vision in this context depends on the area of blockage and the size of the clot.
Blockages that occur in the main vein or artery are more serious compared to those that happen in smaller branches of the veins or arteries.
Discussed Below are Signs of Blood Clot in Eye
1. Blurred vision
This is a common symptom of blood clot in the eye. It is usually not associated with a blood disorder. Most people actually rather link the sign with other health complications such as stress.
A blurry vision may be permanent or temporary, depending on the extent of damage caused by the blood clot within the blood vessels of the eye. In most cases, the symptom usually affects one eye, only the affected eye.
The condition results from the inability of the retina to filter light and communicate to the brain. Having a blurry sight does not have to be accompanied by pain.
2. Pain in the eye
Eye pain can be severe, sharp, throbbing, or aching. In some cases, a patient with a blood clot in eye may feel mild irritation that can be felt on the eye’s surface which seems like a foreign object that has entered the eye.
Eye pain may also come hand in hand with a display of reddening in the eyes, along with blurry vision, or pain that is worsened by direct or bright light. This response to light is due to the fact that the cornea becomes sensitive to pain.
Any disorder that affects the cornea also affects the anterior chamber, causing a spasm of muscles, whose role is to control the iris. In cases of such spasm, any direct or bright light results in muscle contraction that worsens the eye pain.
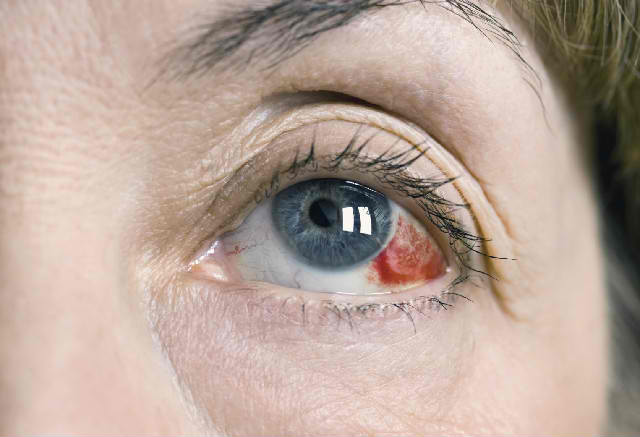
3. Eye redness
Eye redness is the change in color to red of the normally white portion of the eye (sclera). Bloodshot or red colored appearance of the eye happens because blood vessels close to the surface of the eye become wide (dilates).
The dilation can be due to a sudden elevated pressure in the blood vessels of the eye, typically as a result of a blood clot present in an important vessel.
Several critical parts of the eye can be affected. Commonly affected areas include the conjunctiva, the iris, the sclera as well as the episclera.
4. Double vision
A blood clot in the eye can also cause a condition called double vision. Double vision also known as diplopia, entails seeing two images of one same object.
Double vision may form in two ways: Monocular diplopia – present even with only one eye open. The other and more common form is binocular diplopia – present when both eyes are open.
Binocular double vision can be made to disappear when either of the eyes is closed. The problem may last for a few hours but may also become permanent.
5. Watery eyes
The presence of blood clot in eye can cause a disrupted communication between the brain and the eye. The blockage of the blood vessels eventually results to a miscommunication of light that enters the eye then to the brain leading to a watery eye.
This happens due to a wrong signal picked by the lacrimal gland which is located in the outside part of the upper eyelid. It leads to an inappropriate response that results to the production of tears in the lacrimal glands.
6. Sudden and complete loss of vision
An extreme blood clot size in the retina can cause complete loss of vision. Loss of vision may be designated sudden if it develops a few minutes or within a few couple of days.
The loss of vision may either affect one or both eyes. A process that leads to loss of sight may start with a blurred vision that eventually develops into a complete loss of vision. This happens due to total lack of blood supply to the eyes.
7. Eye bulging
A bulge or protrusion on one or both eyes, in a complication known as exophthalmos, is a damaging outcome that can be associated with the formation of blood clot in the eye.
The disorder is caused by the over-reactivity of the thyroid gland towards any formed clot located in the blood vessel regions of the eye. Eye bulging may be accompanied with several other signs and symptoms like pain, redness, and blurred vision.
8. Swelling of the eyelid
An individual may experience swelling in one or both eyelids as a result of a blood clot in eye.
This swelling may sometimes be painless and in most cases, accompanied with itching and pain. Swelling of the eyelid can easily be confused with bulging but the two are distinct from each other.
The swelling may also occur around the eye.
9. Presence of eye floaters in field of vision
Eye floaters are described as specks or tiny strings that appear to be moving through an individual’s field of vision but not corresponding to real external objects.
They are common to represent mild situations of blood clot in the eye. Eye floaters result from the stimulation of the retina by the clot or as a direct effect of the clot; with the brain interpreting it as possible light movements.
In some cases, an individual may interpret the floaters as hallucinations, which is not actually the case.
10. Sudden fluctuations in heart rate
The body will always activate mechanisms that are meant to correct unusual activities in place.
When developed a blood clot in the eye, the brain notifies the heart of the reduced supply of oxygen in the eye. The heart will respond by increasing its work rate to compensate and cover for the reduced oxygen level. This directly leads to an increased heart rate.
- A blood clot in the eye can result from the excessive number of platelets that clump together blocking blood passages
- Blood clots can lead to the loss of vision, either temporary or permanent
- The size of the clot can determine the severity of the symptoms
- The symptoms may not necessarily mean that the individual suffers from a blood clot

- READ MORE