Blood is an essential component of the human body composed of cells and plasma. Plasma is the liquid part that constitutes 55 percent of the blood. The solid part is formed by cells – namely, the red blood cells, white blood cells, and the platelets (thrombocyte cell fragments).
Red blood cells or RBCs are responsible for carrying oxygen to different parts of the body and white blood cells or WBCs are responsible for fighting off infection.
While platelets are needed by the body to stop bleeding. This happens along with other proteins and components in the blood which help in the blood clotting process, known as coagulation factors.
The cellular components of the blood are formed in a sponge-like tissue called the bone marrow which is located inside long bones. The blood cells form and mature in the bone marrow and eventually passed into circulation, in the bloodstream.
However, many diseases can affect production of cells, creating an influence on cellular count such as the platelet count. It will certainly be a horrible position to experience sudden and uncontrolled gushing out of blood from the nose, gums and other openings of the body.
And sadly, it could happen with a really low platelet count. Before that happens, better manage the drop immediately. This may usually be a costly endeavor but there are affordable options such as all-natural remedies you can learn from money back guaranteed materials like Conquer Low Platelets.

A reduced platelet count can only result from three basic mechanisms:
- Reduced production.
- Increased destruction.
- Sequestration or consumption.
All of the diseases listed below fall in at least one of these categories.
Low Platelet Count Causes (By Medical Condition)
The following medical conditions are observed to cause a low platelet count:
1. Dengue Fever.

Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by a viral infection. Some patients experience the development of the condition into a life-threatening stage referred to as dengue-hemorrhagic fever, where bleeding, blood plasma leakage, and low platelet count takes place.
The drop in platelet levels is a result of the attack brought about by the virus against the tissue where platelets are produced, the bone marrow.
The treatment for acute dengue is supportive in approach, using either oral or intravenous rehydration for mild or moderate cases. Intravenous fluids and blood transfusion are included in severe cases of the medical condition. Hospitalization is required in the management of dangerously low platelet count.
2. HIV infection.
HIV is a rapidly spreading viral infection that also causes a reduction in platelet count. HIV can affect any organ of the body which includes the bone marrow, altering platelet production.
The treatment of HIV-induced reduction in platelet count is called HAART or Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy. It is aimed at reducing the viral load and preventing further destruction of the bone marrow by giving time for the platelets to revive.
3. Drug-induced.

Certain drugs such as paracetamol, diclofenac, fluconazole, ibuprofen, naproxen, etc. can cause low platelet count in different ways. Withdrawing the causative drug is the management of choice for a drug-induced low platelet count.
In some cases, the platelet count may fall dangerously low and the patient may require hospitalization. The treatment may be refocused on management of any developed complications along with effectively preventing death.
4. Heparin-induced.
Heparin is a drug used in thrombotic situations such as pulmonary thromboembolism. A thrombotic state is a situation when abnormal blood clots form due to certain factor/s. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia or HIT is different in the way it causes low platelets in comparison to other drugs.
In fact, heparin can cause an increased tendency of forming more blood clots as opposed to increasing the chances of bleeding. This may sound contradicting but it does happen in many occasions. The reason it happens is centered on HIT antibodies that may have formed against platelet protein which eventually activates the platelets.
The activated platelets cause increased clot formation, while consuming a lot of platelets in the process, resulting to a low platelet count.
5. Idiopathic or Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura.
ITP is an immune mediated causative factor for reduced platelets in the body. It is defined as the occurrence of isolated low platelet count but with a normally functioning bone marrow and the absence of other causes of thrombocytopenia such as secondary immune-, drug-, or viral-induced cases. The destruction of platelets takes place in the bloodstream and the spleen.
ITP causes a characteristic purpuric rash along with an increased tendency to bleed. This autoimmune condition that causes the destruction of blood platelets in patients is classified as primary thrombocytopenic purpura. Read about ITP treatment methods.
6. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura.
TTP is caused by a deficiency of an enzyme that cleaves von Willebrand factor. It can also be a result of a destruction of the enzyme by antibodies.
Von Willebrand factor, when cleaved, acts upon platelets, normally preventing adhesion and aggregation, to keep blood from clotting together as it should in normal circumstances. This keeps the blood flowing freely in the bloodstream.
In the absence of the cleaving, however, the platelets adhere and aggregate to one another forming blood clots. This leads to increased consumption of platelets resulting to a low platelet count. TTP can be inherited or idiopathic. The inherited form of the disease is called the Upshaw Shulman syndrome.
7. Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome.

HUS is mostly preceded by a severe and ignored case of bloody diarrhea. This results in reduced blood flow to the kidneys due to severe dehydration which may eventually lead to kidney damage.
The loss of blood through the gut in the form of diarrhea is directly responsible for the reduced platelet count in HUS. There is another form of HUS which is hereditary in nature and not associated with diarrhea.
The treatment is supportive and revolves around correction of dehydration and prevention of complications that can take place due to reduced platelets.
8. Pregnancy-induced.
Reduced platelets in pregnancy can be due to medical conditions such as connective tissue disorders, viral infections, and hypersplenism. But the most notable of disorders is HELLP syndrome.
This can result from the increase in blood pressure which is directly influenced by the course of pregnancy itself. It is usually managed with intake of drugs, safe for use during pregnancy, like magnesium sulphate that lowers blood pressure levels. However, there are cases of mild drops in platelet count during pregnancy that can be considered normal.
9. MYH9-related disorders.

Myosin heavy chain 9 (MYH9)-related platelet diseases belong to the group of inherited thrombocytopenia. May Hegglin anomaly, Sebastian, Epstein and Fechtner anomalies however, are rare causes of reduced platelet count.
Each of these has a common feature – the presence of large platelets as can be seen on microscopy. But their distinctive features differentiate one from the other. These diseases can be inherited in any one of the many forms such as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked recessive.
10. Evans syndrome.
This is a disease that presents a diagnostic dilemma even to many physicians. It is very similar to HUS in presentation. Evans syndrome can only be differentiated by a blood test called Coombs test.
The main complication of low platelet count is the tendency to bleed, but depending on the location of bleeding, it will produce different symptoms. For example, if the bleed occurs inside the brain, the symptoms will be nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, etc.
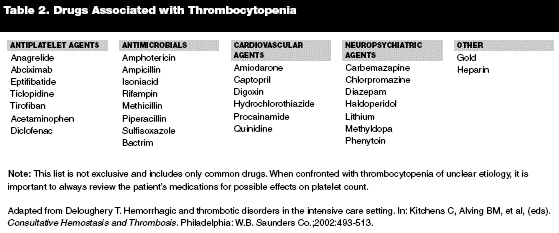
The medical disorders that may result to a display of reduction in platelet count are not exclusive to the list above but many cases fall under one of these. As true for a lot of diseases, not every condition can be conclusively diagnosed and treated for good, but can be managed. The management of low platelet count is grounded on the associated underlying specific medical condition.
- READ MORE