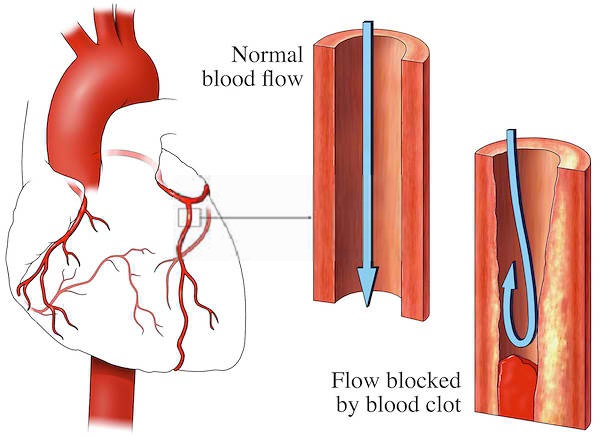
The formation of a blood clot is normal when the process is needed to stop the loss of blood in response to injury of the blood vessels. But in certain situations, where the body produces an excess in the number of platelets, the clotting process can be altered.
Platelets are components of the blood responsible for blood clotting. In increased amounts, platelets develop a potential to clot abnormally within the blood vessels.
Unnecessary blood clotting takes place even when damage is not sustained by body tissues. When this happens, blood clotting will not be serving the normal function of protecting the body from excessive loss of blood but instead becomes a threat to the body.
The complications that can result from abnormal clotting depends on the location where the clot has formed. Blood clots can be very dangerous when formed in blood vessels, while causing an obstruction. It can even reach to an extent to be life threatening to the patient. For example, a blood clot that forms in the heart places the patient at risk of a heart attack.
Possible Signs and Symptoms of Blood Clot in Heart:
1. Chest pain
A person with a blood clot in the heart is likely to experience episodes of chest pain. The onset of pain happens without any other external causative factors such as injury.
The pain also differs in degree. To some patients, the pain is extremely sharp and burning. To others, the pain is not focused and only experienced intermittently, suddenly reappearing from time to time. This type of pain is usually felt when coughing or taking a deep breath.
2. Rapid breathing and shortness of breath
An individual with a blood clot in the heart is likely to breathe rapidly as the body tries to ensure that every tissue receives enough oxygen-rich blood. This happens because the blood clot usually creates a blockage against adequate flow of blood to body tissues or rather, causes the heart to become unable to pump enough blood into the lungs.
This makes most of affected body tissues lack the amount of oxygen needed to function, important in most metabolic activities. Therefore, the body will try to offset the decrease in oxygen supply by increasing the amount of air getting out and into the body during respiration.
3. Fainting
Fainting is also caused by the lack of sufficient supply of oxygen to the brain, leading to a failure in optimal performance of brain functions. The inadequate supply of oxygen to the brain may indicate a limited flow of blood via the carotid artery.
When the flow of blood, either into or out of the heart is reduced, the brain can be affected and inadequate supply of enough oxygen becomes possible. This can result to fainting. If the shortage of oxygen supply is not addressed as appropriate, it can lead to complications that can be life threatening.
4. Changes in body temperature
A blood clot usually leads to a change in the body temperature of the patient. This results from the restricted flow of blood considering that it is also responsible for the distribution of heat throughout the body.
The temperatures will be high in some parts while other areas will be low as they don’t receive enough blood supply. The increase in temperature may only occur for a short time.
5. Vision problems
The blood that carries oxygen also travels to the occipital lobe at the back of the brain. This is a part of the brain that coordinates vision.
When the body does not provide sufficient blood to the occipital lobes of the brain and oxygen supply is not enough, the ability of the patient to see will be affected. The coordination between the brain and the eyes will not be effective.
The patient may experience partial blindness such as blurry vision or double vision that can eventually result in complete blindness when treatment is not given in time.
6. Fever
The changes in body temperature will likely result to a fever. This can be observed when the body of the patient displays sweating, shivering, and a general increase in body temperature. The fever may only be mild.
The onset of fever is commonly accompanied by a lack of appetite and presence of headaches.
7. Pain in other body areas of the body
Apart from the pain experienced in the chest, other body areas may also develop some pain. The pain can be acute and in some cases, very progressive in characteristic leading to the discomfort of the patient.
Pain may be felt in the upper portion of the abdomen. Also, it may be develop in the left arm first before being felt in the right arm, but happens rarely.
8. Rapid heart rate
The heart will also increase the rate at which cardiac muscles relax and contract to try and force blood through the blocked blood vessels. This can be observed when the heart beats faster compared to the usual rate.
The size of the clot will influence the rate of heart beat. A smaller clot may only display a small change that might not be even considered significant. However, when the blood clot is large, to almost completely block the entire lumen of the blood vessel, the heart will work faster in order to try in eradicating the clot.
9. Fatigue
The presence of blood clot in the heart compels body systems to become overworked and exhausted in trying to resolve the problem.
In addition, the lack of enough oxygen required for the production of energy can lead to slow or completely deprived body cells. In later stages, the whole body may experience general body weakness which can be progressive.
10. Paralysis
Some body parts may result to a paralysis due to the lack of enough oxygen reaching the brain as a complication of the blood clot. Lack of oxygen in the brain can make the capacity for motor and sensory functions to fail considering that the source for body coordination is the brain.
Since the heart has the sole responsibility of pumping blood to every part of the body, a failure affects almost every area that relies on oxygen in carrying out each of their functions.
The paralysis may either be experienced by the patient entire the body or just parts of it. The most common body parts affected by paralysis are the arms and legs.
It is important to seek medical assistance should any of the above signs is experienced.
Notes:
- Blood clotting in the heart can lead to a heart attack
- Inadequate function of the heart can lead to the failure of affected body organs
- Common signs of blood clot in heart include chest pain, upper body discomfort, and shortness of breath
- READ MORE